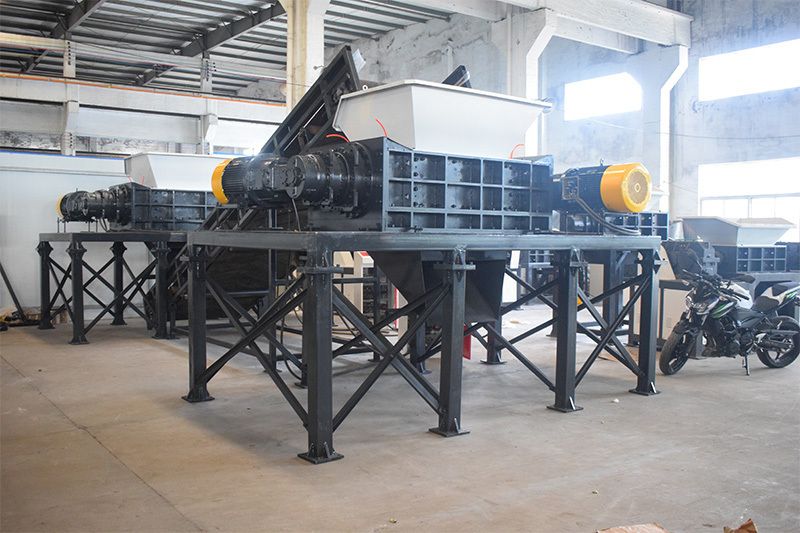
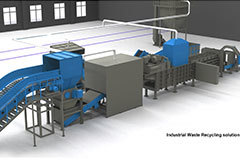
General industrial solid waste pretreatment scheme

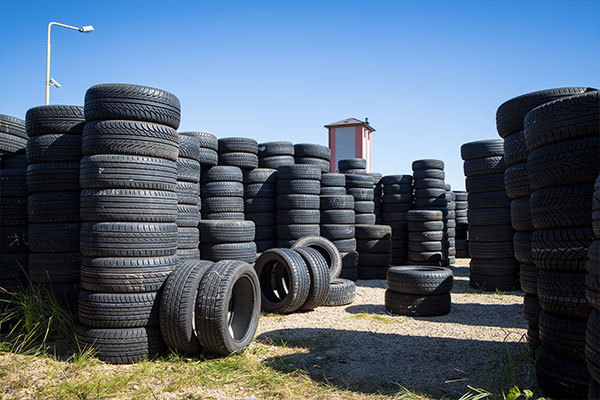
The total amount of waste tires produced in my country has ranked among the top in the world for many years. According to the information released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, about 330 million waste tires were produced in 2019, of which about 290 million were used car tires, accounting for 88%. my country's waste tire production will continue to grow, and is increasing at an annual rate of 8% to 10%.
Waste tires are called "black pollution", and the accumulation of a large number of waste tires not only occupies land but also seriously damages the environment. Due to the uncertainty of the time it takes for tires to decompose, waste tires are not biodegradable, and their components include elements such as lead, chromium, cadmium and other heavy metals, which can pose a threat to human health and the environment if not properly handled and managed. Waste tires stacked in the open air for a long time will not only occupy a large amount of land resources, but also easily breed mosquito-borne diseases, seriously deteriorate the natural environment, and pose a fire hazard. Therefore, how to dispose of the increasing number of waste tires has become an urgent environmental problem and a development problem of supporting industries.
Waste tires can be treated in various ways, such as prototype utilization, retreading, recycling, auxiliary fuel, and thermal cracking and power generation technologies:
1. Recycling
Waste tires can be pulverized into rubber powder, which is widely used in highways, airstrips, flame retardant materials, rubber and plastic soles, waterproof materials, sports runways and other fields. Rubber powder can also be desulfurized and used to make rubber products such as hoses and tapes.
2. Auxiliary fuel
The calorific value of waste tires is more than 8000 kcal, which is higher than 5000 kcal of coal, and the residual ash after combustion is also equivalent to that of coal, so it is very suitable for industries that require high heat energy. In the United States, Japan and many European countries, many cement plants, power plants, paper mills, steel plants and smelters use waste tires as fuel, with good results, reducing production costs to a certain extent.
3. Thermal cracking
The principle of thermal cracking is to place waste tires in an oxygen-deficient or inert gas for incomplete thermal degradation, which can produce liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons and carbon residues. In this technology, the waste tires are first crushed into blocks and then sent to the thermal cracking reactor. After heating in the reactor, a thermal decomposition reaction occurs. Next, the gaseous products are separated from oil and vapor through a condenser, and the fuel oil is condensed and used as fuel. In addition, the separated non-condensable combustible gas is sent to a combustible gas generator for power generation through desulfurization treatment, which solves the problem of secondary air pollution. Except for a small amount of electricity for thermal cracking system equipment, most of the power can be connected to the grid for power supply. , the solid product in the reactor is mainly carbon black, and the crude carbon black is separated from the steel wire by magnetic separation, and the crude carbon black is further processed to obtain carbon black for commercial application.
Tire crushing process flow chart

Waste paper products

Factory waste

Rags/textiles

Waste paper products

Factory waste

Rags/textiles
WASTE TIRE TREATMENT SYSTEM
At present, more than 200 large and medium-sized cities in my country generate more than 1.3 billion tons of general industrial solid waste every year, including a large number of waste paper products, waste plastics, rags and various textiles, waste rubber, broken leather products, waste wood and other high-heat worth waste. On the one hand, the composition of materials is complex and diverse, and most of them have the properties of high strength and good toughness, which makes pretreatment difficult, especially the difficulty of crushing and processing. Therefore, a large part of solid waste with high calorific value is disposed of in landfills, resulting in waste of resources; On the one hand, these high calorific value solid wastes are high-quality "alternative fuels (SRF/RDF)" once they are pretreated to the appropriate particle size.
At present, with the scarcity of resources, the deterioration of the environment and the improvement of people's awareness of environmental protection, the world has put forward a clear task of CO2 emission reduction. On the one hand, the use of SRF/RDF to replace fossil fuels can reduce CO2 emissions and benefit from CO2 emission credit trading activities, because the CO2 emissions of SRF/RDF are much lower than those of fossil fuels; on the other hand, various kilns simply increase the input The material device can co-process SRF/RDF, and at the same time, it can obtain policy support and benefit from environmental protection.